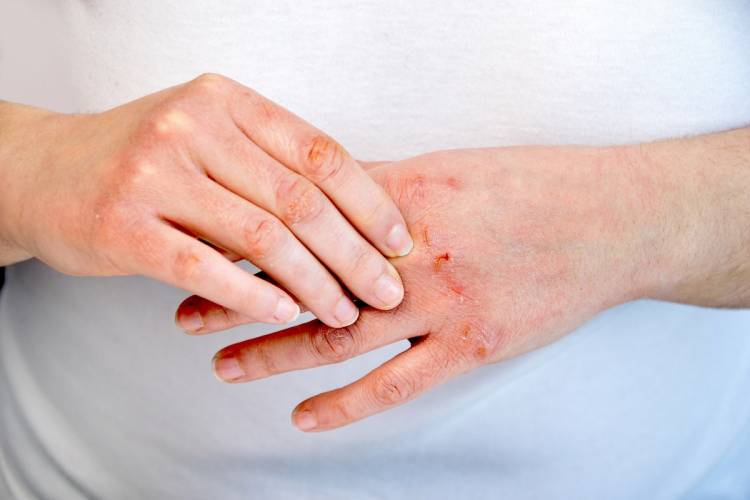
The term dermatitis refers to inflammatory processes of the skin on the face or body, regardless of their cause. Most often, it involves damage to the epidermis and the underlying layers of the skin due to negative environmental factors such as temperature extremes, humidity fluctuations, exposure to chemical substances in gaseous, liquid, or dusty form, as well as mechanical damage (minor wounds, scratches, friction, itching).
In addition, dermatitis may be a manifestation of allergies or infectious diseases, the effects of parasites, or insect bites.
The main symptoms of dermatitis include redness of the skin or various types of rashes, as well as dryness, pain, and itching. Blisters, cracks, or oozing lesions may also occur. Dermatitis can be acute and short-term or develop into chronic skin damage.
Common Causes of Dermatitis
Among the many causes, infectious factors, allergic reactions, and environmental influences are the most common. The following categories are typically distinguished:
Obligatory (irritant) factors
These cause dermatitis in anyone upon contact with the skin, even in completely healthy individuals. This group is generally referred to as contact dermatitis (which may also include infectious forms).
Optional (individual) factors
These cause inflammatory reactions only in certain individuals—such as people with allergies, children, individuals with sensitive skin, or older adults. These forms are often classified as eczema or allergic dermatitis.
Triggers of Contact Dermatitis
The most common provoking factors include:
Friction or pressure on the skin, scratches, minor wounds
Burns or damage caused by footwear
Sun exposure (both ultraviolet and thermal radiation)
Exposure to electric current
Contact with aggressive chemicals (acids, alkalis, heavy metal salts, caustic compounds)
Toxic substances, fuels, and hydrocarbons
Rubber and latex products; components in clothing or footwear (chromium or nickel)
Certain types of plastics and synthetic fabrics
Cosmetic products, detergents, cleaning agents, bleaching products, disinfectants
Plant juices (grass, nettle, alkaloids)
Certain medications (liquids, powders, ointments, creams)
Contact with formaldehyde, turpentine, irritating compounds, or capsaicin (pepper extract)